Keyword Mapping: What It Is and How to Map to Your Purchase Journey
Topic: SEO
Published:
Written by: Brandon Leuangpaseuth
You’re tasked with increasing organic traffic to your blog. Piece of cake, right?
Prioritize your keyword list by volume and start writing. Wrong!
Instead, you need to map your keywords to your customer journey first. But how?
You’ve come to the right place. Keep reading to learn why keyword mapping is essential, how to map keywords, keyword cannibalization, and how to effectively outline your customer’s journey.
Let’s dive in.
What is keyword mapping?
Keyword mapping is researching and matching your target keywords with landing pages.
By mapping out keywords, you’ll be able to:
see where your site currently stands
avoid the pitfall of keyword cannibalization
develop an effective content marketing/SEO strategy
Why is keyword mapping important?
Keyword mapping organizes your site's pages and establishes each new page's purpose. You can adequately track page performance after you map keywords.
The benefits include:
Organized content strategy
Overhead view of your search engine optimization (SEO) strategy
Promote internal link-building optimization
Prevent keyword overlap
Organized content strategy
You are able to discover missing keyword opportunities and target them with relevant pre-existing or new pages by keyword mapping.
Overhead view of your SEO strategy
You’ll plan out pages to rank for the right keywords. And quickly see if terms are too broad, don't match search intent, or are too competitive to even bother with.
Promote internal link-building optimization
When you know what pages should be ranking for which keywords, you can send the correct signals to match the target keyword
You’d be able to make the proper on-page SEO optimizations to improve the page's relevance to the mapped keyword.
For example, if you know a page should be ranking for the keyword, “1099 expense tracker”, you can add internal links from other pages to your site with the anchor texts:
track 1099 expenses
1099 expense tracker app
1099 tracker
expense tracker for 1099
Knowing what each keyword a page should rank for would also prevent you from sending signals to the wrong page i.e. you would not use the anchor text “1099 expense tracker” to point to a page where you are trying to rank for the keyword “quarterly taxes”.
This is particularly important for tracking page performance and guiding anchor text selection for on-page SEO.
Prevent keyword overlap
When you organize what keywords your pages should rank for, you can prevent keyword cannibalization. Later, we’ll review what that means and how it can hurt your rankings.
How to do keyword mapping
The first thing you need to do in creating a keyword map is to open up your favorite spreadsheet document (we use Google Sheets). The spreadsheet should include the keyword, organic search volume, keyword difficulty, and what page should rank for it.
Now that you have your sheet, let's go through each step to build a list of relevant keywords, organize them, and create potential page URLs.
Step #1: Research, plan, and make a list of your target keywords
Use our Topic Exploration tool or one of the other SEO tools below to perform keyword research:
Google’s free keyword planner (you’ll need to create a Google Ads account).
InfiniteSuggest
Keywordtool.io
UberSuggest
Semrush
Soovle
Ahrefs
Moz
In this example, we’ll use Clearscope and Ahrefs.
Discover relevant keywords
The first thing you should do is carefully analyze your niche’s relevant keywords and your competitors. Enter your search query into the search bar and select the search engine filters like which search engine, country, etc.
Type in the term and navigate to Related Keywords and Search Suggestions to collect keywords and phrases.
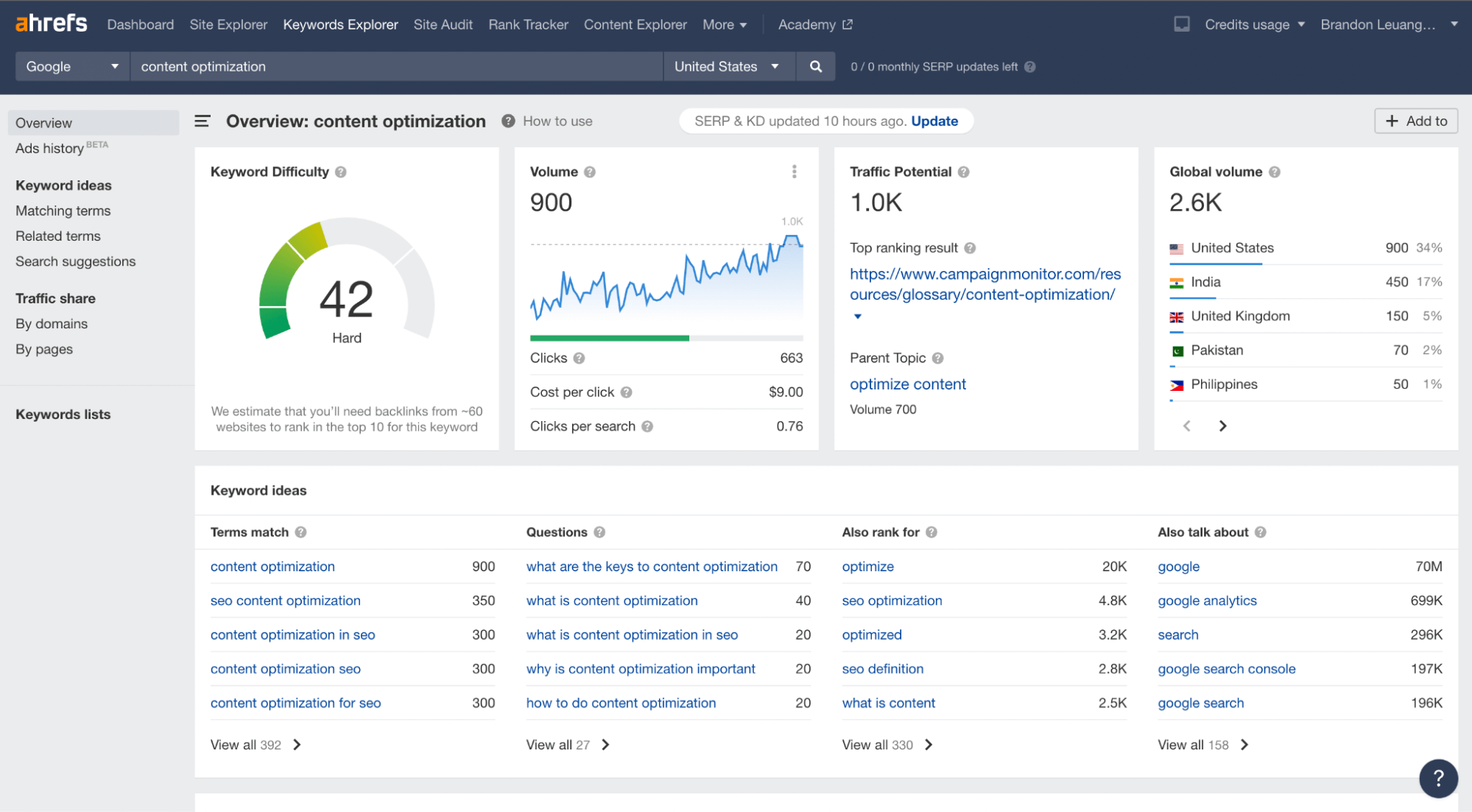
A search for “content optimization” in Ahref’s Keywords Explorer.
You can sort the keywords by monthly volume, competition, number of backlinks you’ll need to rank, and add filters for your queries.
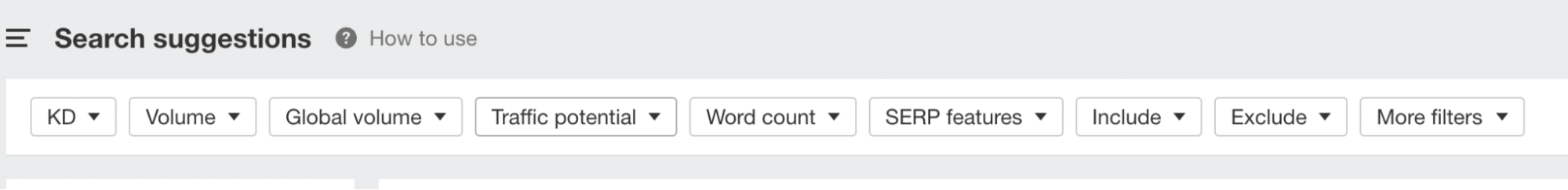
The Search Suggestions in Ahrefs.
Cherry-pick keywords you believe your business is worthy of ranking for. When you select keywords, consider the competition, keyword difficulty, search volume, and intent.
Then, input the keywords and their relevant data onto your sheet.
How to discover keywords with Clearscope
You could have the most stellar piece of content, but your potential to rank well for a term would be limited if you do not match the search intent behind the query. Our Topic Exploration tool is valuable for combining search intent with keyword data.
For example: If you wanted to write a post about electric toothbrushes, you might begin with the keyword “electric toothbrushes” to discover the most popular searches for the query.
Afterward, you can analyze the keyword opportunities that are more relevant to your specific topic: best electric toothbrush
Our tool will save you time manually analyzing the search engine results page (SERPS) to determine the search intent.
Here’s how to do it with Clearscope. First, navigate to the Topic Exploration feature in Clearscope, and type the keyword.
Clearscope’s Topic Exploration.
You’ll see a page that looks something like this after you click “Run”.
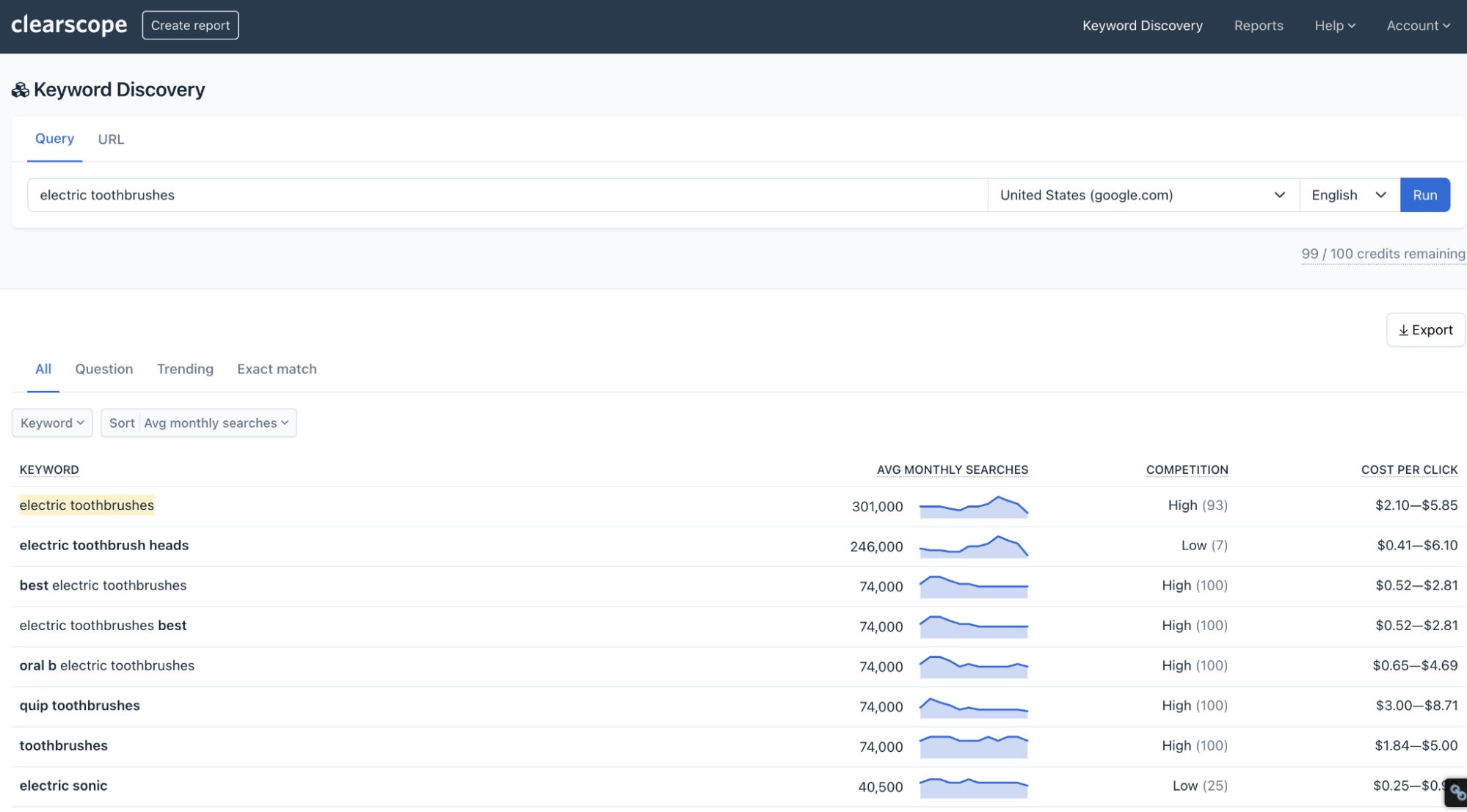
A search for “electric toothbrushes” in Clearscope’s Topic Exploration.
You will get metrics like related keywords, search volume, and competition from our tool.
There are also tabs for “Question,” “Trending,” and “Exact Match” for more keyword ideas.
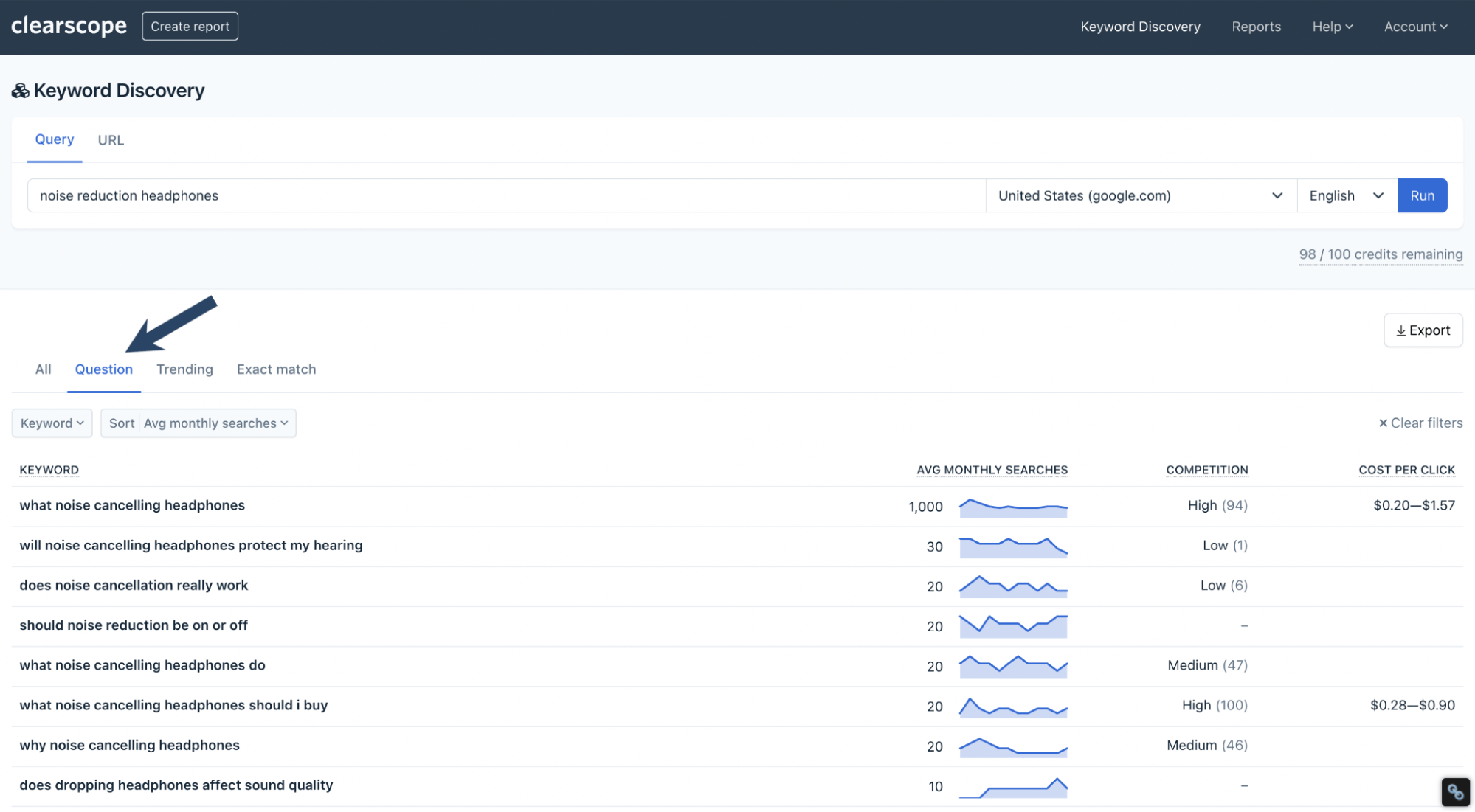
A search for “noise reduction headphones” questions in Clearscope’s Topic Exploration.
Recommended reading: On-Page Optimization Tools to Create & Update Site Content
Analyze competitors
Increase the number of relevant keywords by looking at competing websites and how the competitors structured their keyword map.
See what keywords they rank for, keyword gaps, content gaps, track competitor performance and better understand you and your competitors' audience.
Let’s dig into how to uncover competitors.
Run a related search
Google Search Operators can quickly find related websites. Use the search query: related:yourwebsite.com.
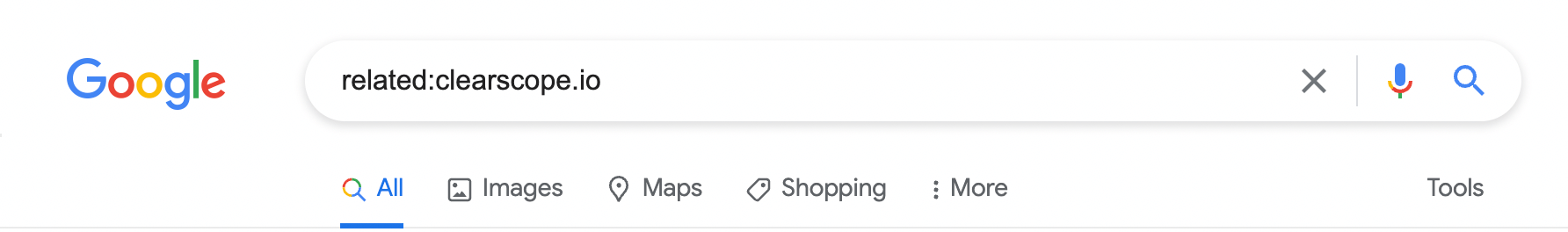
A Google search for “related:clearscope.io”.
Depending on your industry and niche, this option may not attract many good competitors. For example, if your product is in a new industry or your site does not rank for many keywords, there may not be many results here.
You can also discover competitors using SEO tools such as Ahrefs, Moz, and Semrush.
See who is ranking for the top keywords in your niche
You can look at competing domains already ranking for keywords by using different SEO tools. Ahrefs’ Site Explorer enables you to find competing domains. You’ll discover competitors with overlapping keywords. Use the Keyword Explorer tool to research if your site is not ranking for many keywords.
Step #2: Group similar keywords and match search intents
Grouping similar keywords and search intents are essential in generating content.
Group related keywords in the template section to rank for one page. A page could have a primary target keyword and multiple secondary keywords.
Secondary keywords include synonyms, subtopics, and long-tail keyword variations.
For example, you could have a single-page ranking for the keywords:
“personal injury lawyer San Diego” & “personal injury attorney San Diego”
"noise reduction headphones” & “noise cancellation headphones”
You may map multiple keywords to one page. However, multiple pages should not rank for the same keyword.
It’s simple to create semantic keyword groups. We’ll show you how in the next section.
How to find secondary and related keywords
Discover secondary keywords by running your primary search term through our Topic Exploration tool.
Group similar keywords with matching search intents.
Here’s an example for “noise reduction headphones”
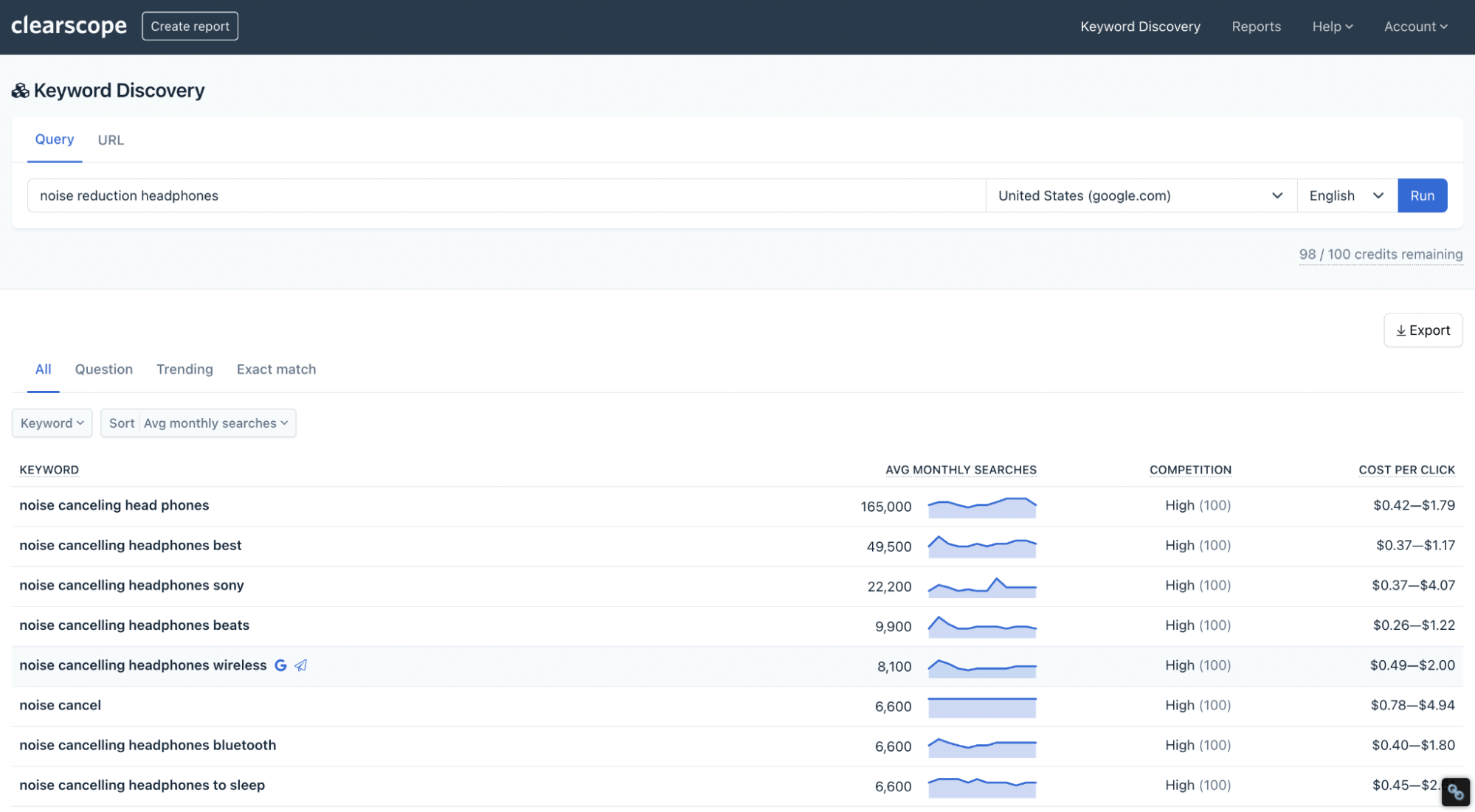
A search for “noise reduction headphones” in Clearscope’s Topic Exploration.
Google-related search suggestions
When a user searches on Google, the search engine will return a list of related searches at the bottom of the SERP.
Here’s what it would look like for the keyword “link building.”
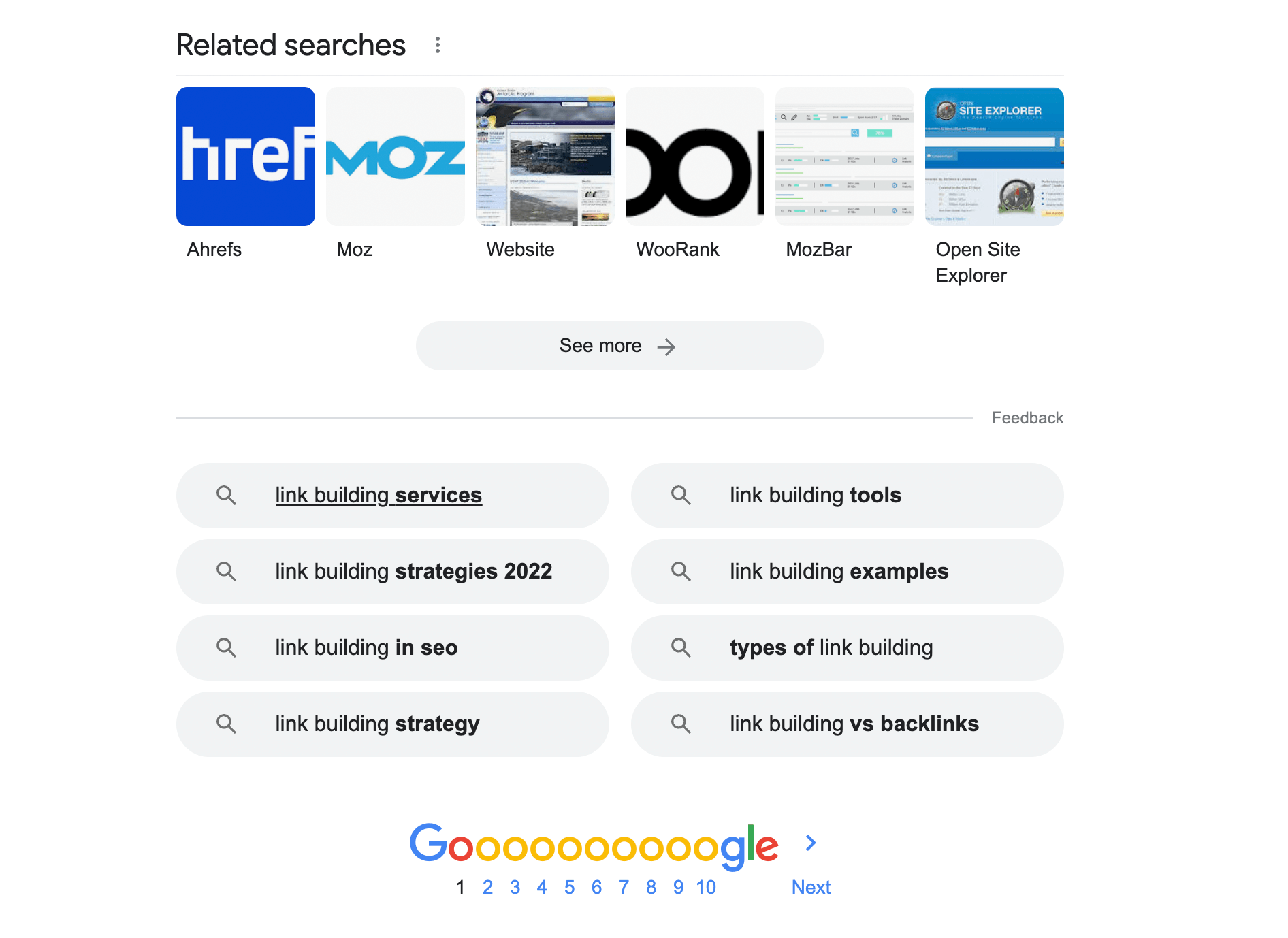
Google’s Related Searches for a search for “link building”.
These suggestions are a great way to get ideas of what Google thinks queries related to the keyword are.
Google SERP tactic
Try this if you get stuck wondering if you should create two pages for separate keywords or one.
Search both keywords on Google. Here’s an example for the keywords: “benefits of incorporating” and “pros and cons of incorporating.”
They are very similar in search intent.
I’ll plug both keywords into Google and analyze the results.
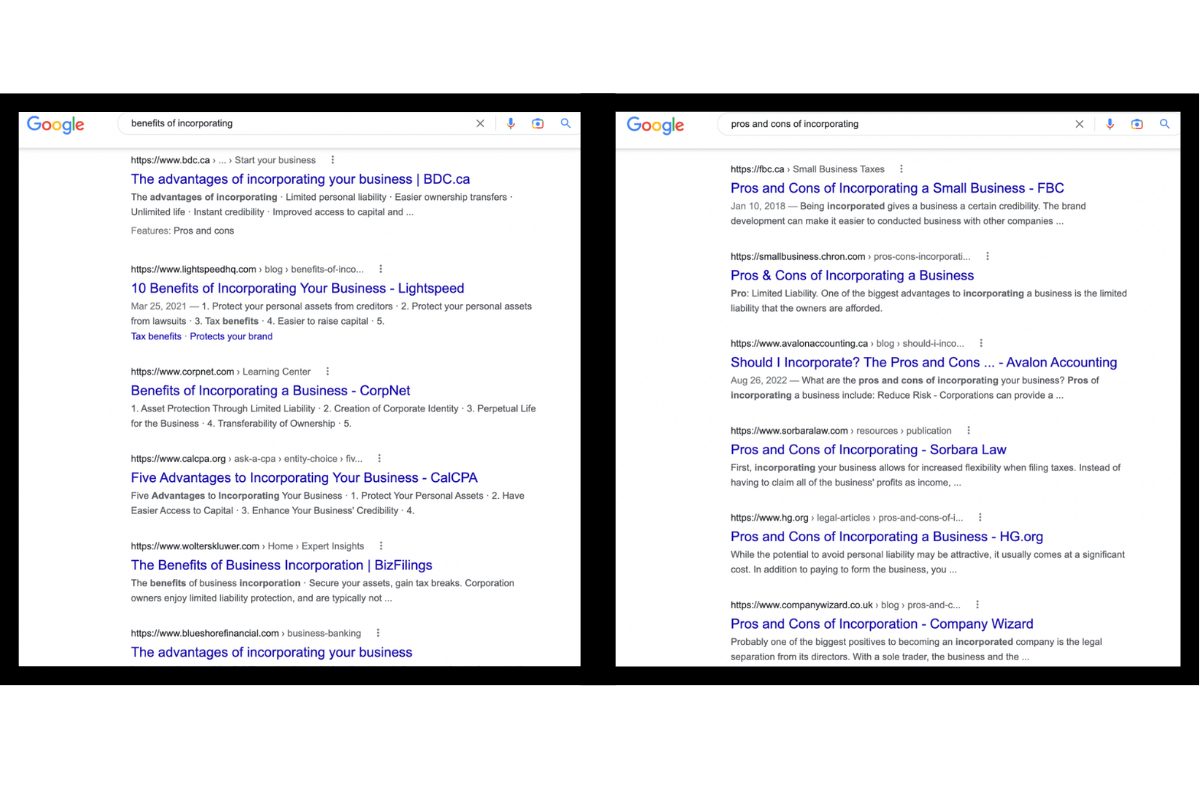
Google searches for “benefits of incorporating” and “pros and cons of incorporating”.
As you can see, different pages rank at the top for these two keywords. In this case, I would produce two different pages instead of trying to target them both with one page.
Alternatively, if you see the same web pages for the two different keywords, you could create one page to rank for both.
Step #3: Create potential URLs & title tags
Once you’ve researched and grouped keywords, create potential page URLs and title tags. Observing your competitor's page structures is a great way to get ideas.
In the next section, we’ll show you how to get URL and title tag ideas from your competitors.
URL tips
Get ideas for your keyword map by running a competitor page structure analysis. You’d understand how a good page structure should be laid out.
Here’s how to do it for free using Screaming Frog.
Simply plug your competitor’s site into the tool. Click on “Internal”—> “HTML”—> “Export”.
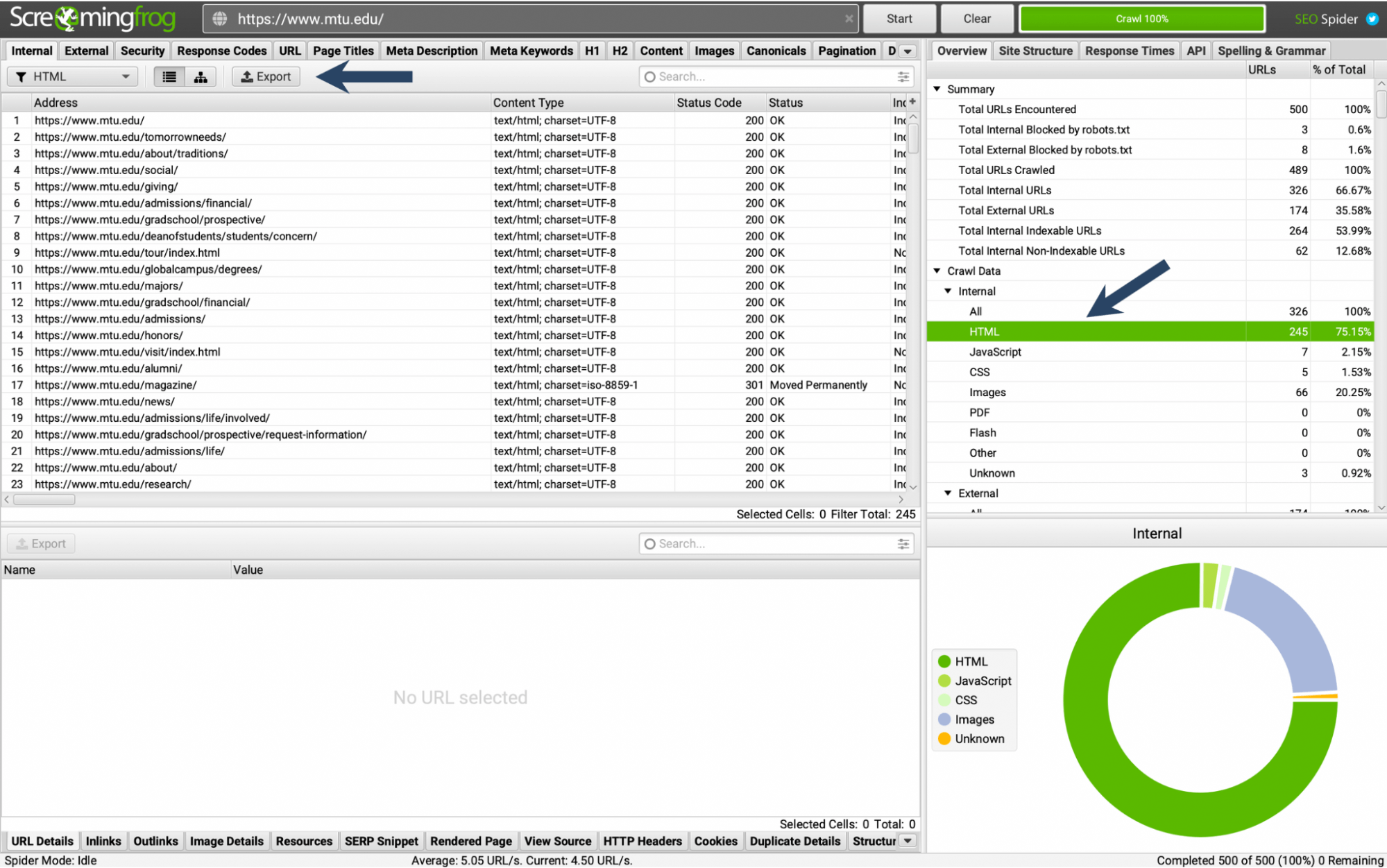
Screaming Frog search for “https://www.mtu.edu”.
Once you export their pages, you’ll see how their URL structure and title tags.
A tool like Ahrefs can show you what page is ranking for a keyword. Plug in your competitors' URL in the site explorer. Click on “organic keywords” and then “Export”.
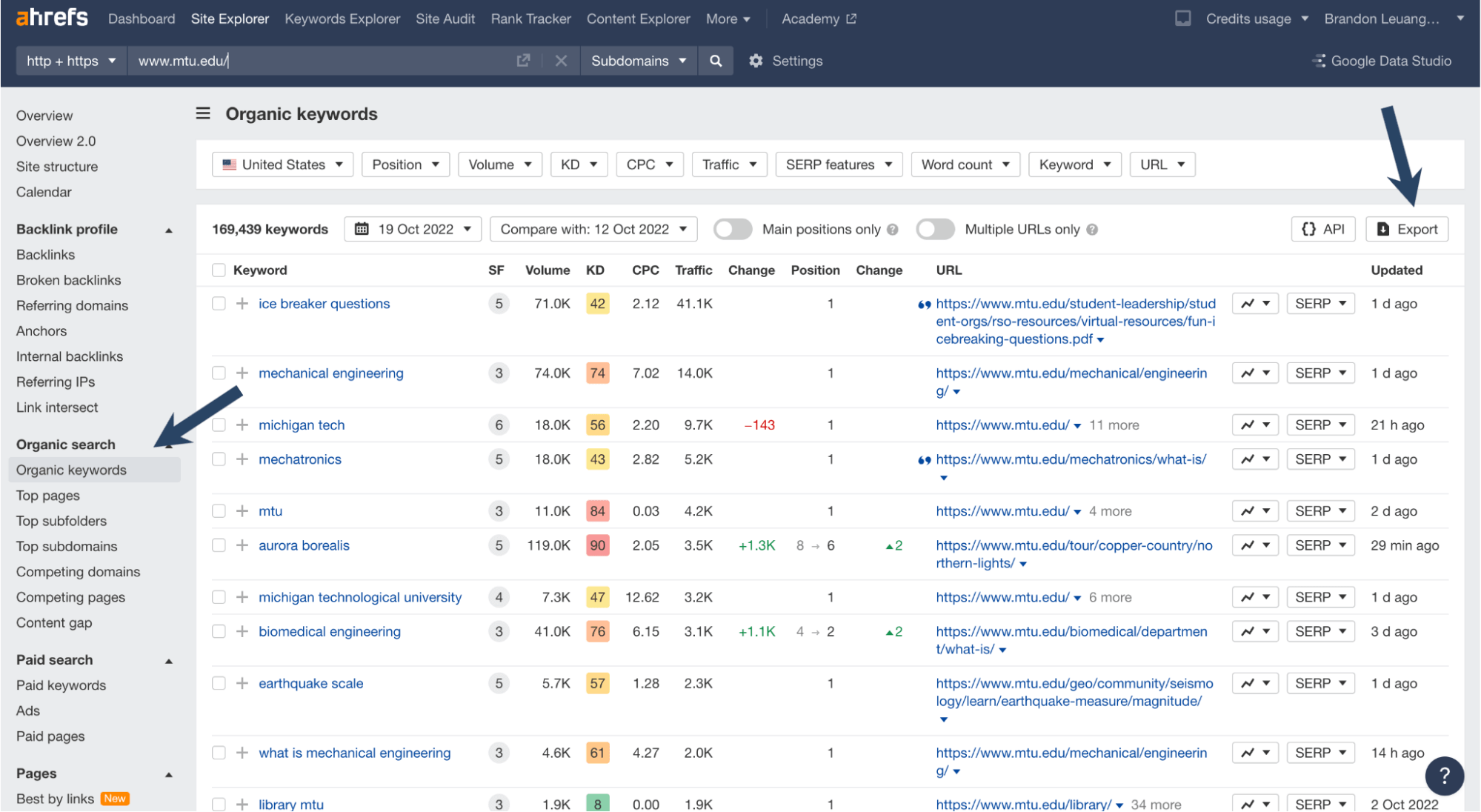
An Organic Keywords search for “www.mtu.edu” in Ahrefs.
You’ll see which pages rank for what keyword on the site.
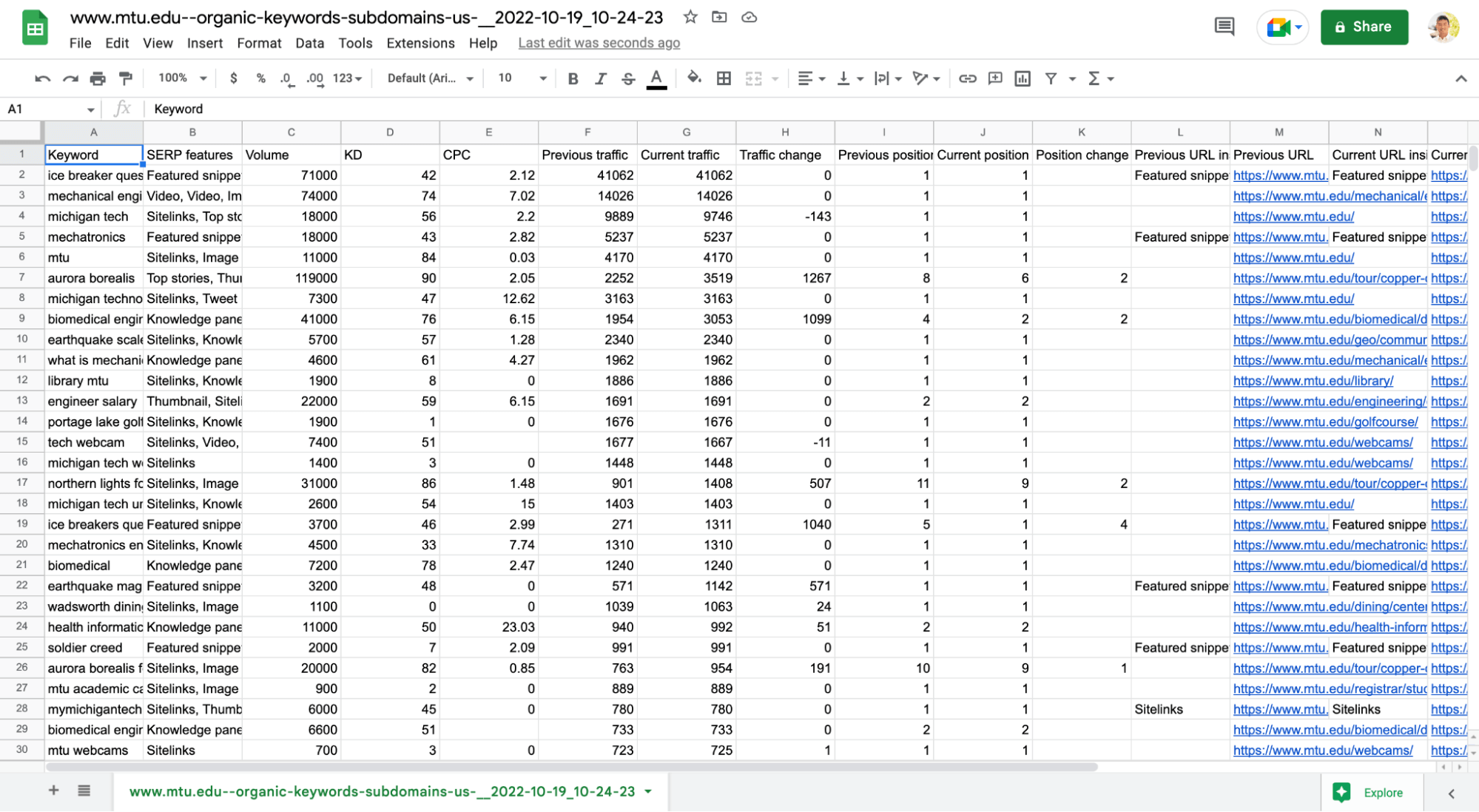
An export of organic keywords from an Ahrefs search for “www.mtu.edu”.
Title tag tips
Capture multiple target keywords for one page by creating the correct title tags. Write out a title tag to combine your primary keyword with your secondary one.
Here’s an example with the keyword: electric toothbrush on plane
Related keywords with the same parent topic are:
can i bring an electric toothbrush on a plane
Here’s what the final SEO title tag could be:
Can You Bring An Electric Toothbrush On A Plane?
Some tips for optimizing your title tags:
Write naturally in a way that makes sense
Try to include the exact match of the primary keyword
Do not repeat keywords
Try to keep the target keyword close to the front of the title tag
Stay within the 60-character limit
Use Screaming Frog to review your competitor’s title tags. Click on the tab “Page Titles” and look at “Title 1”.
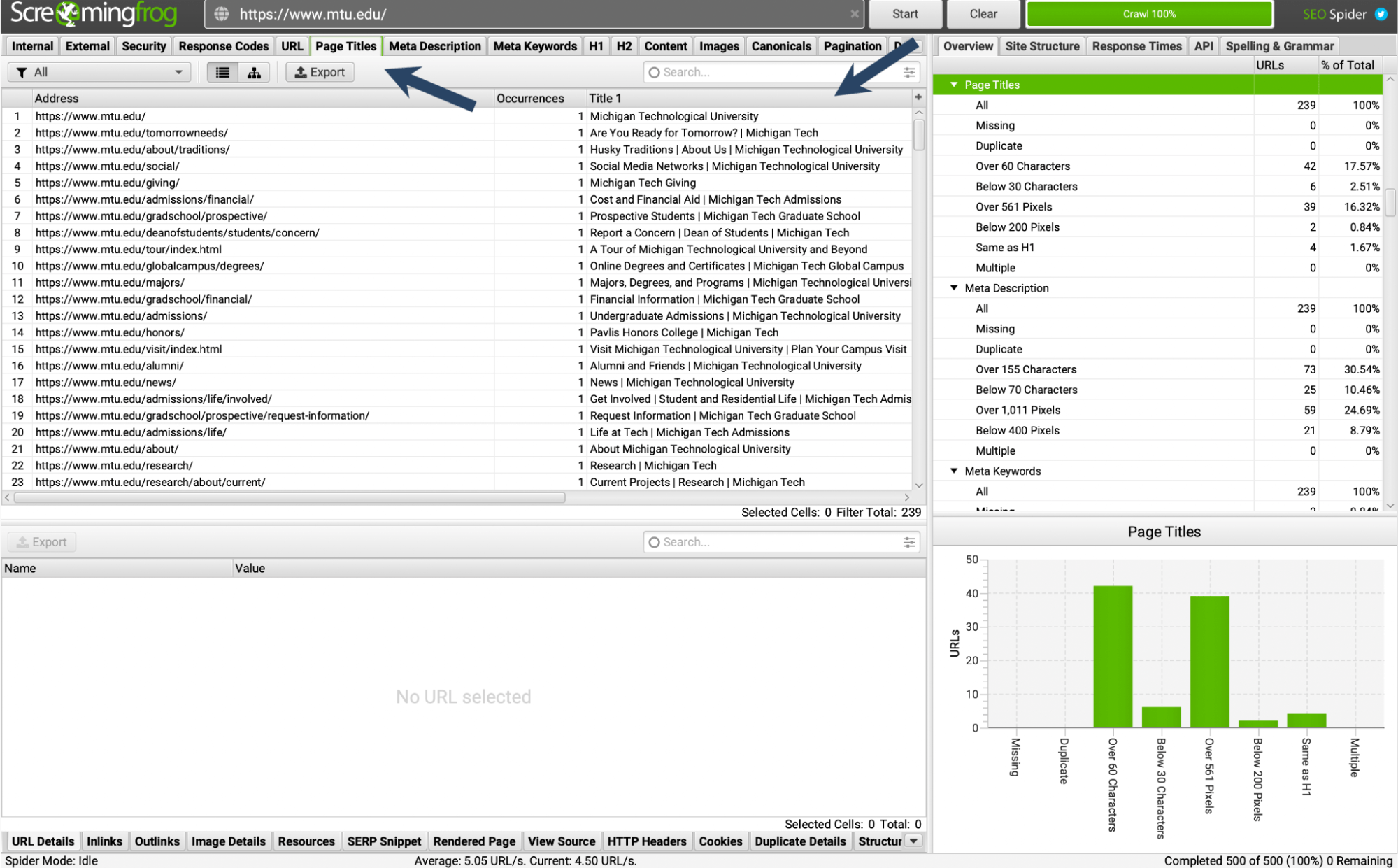
Screaming Frog search for “https://www.mtu.edu”.
Audit your site for keyword overlaps and duplicates
When you create your keyword map, you’ll want to audit your current site structure. You’ll avoid duplicate content, and have your pages compete against one another or keyword cannibalization.
Keyword cannibalization
Keyword cannibalization is when two or more pages on your website use the same target term and show up for the exact searches. As a result, the pages sometimes struggle to rank at their full potential.
When multiple pages compete against one another to rank for the same keyword, the pages become diluted with power, and every page becomes less visible to Google. In other words, when multiple web pages seem too similar, it can confuse and send negative signals to Google.
This is why keyword mapping is so important—it prevents different pages from competing for the same keyword. So, instead of having multiple pages rank on the second or third page of Google, you’d have one ranking on the first page.
We’ll quickly review a few tactics to diagnose and fix keyword cannibalization.
Search Console tactic
Register your website on Google Search Console to help you detect keyword cannibalization.
Just follow these simple steps:
Login into your account in the section "Search Results > Queries".
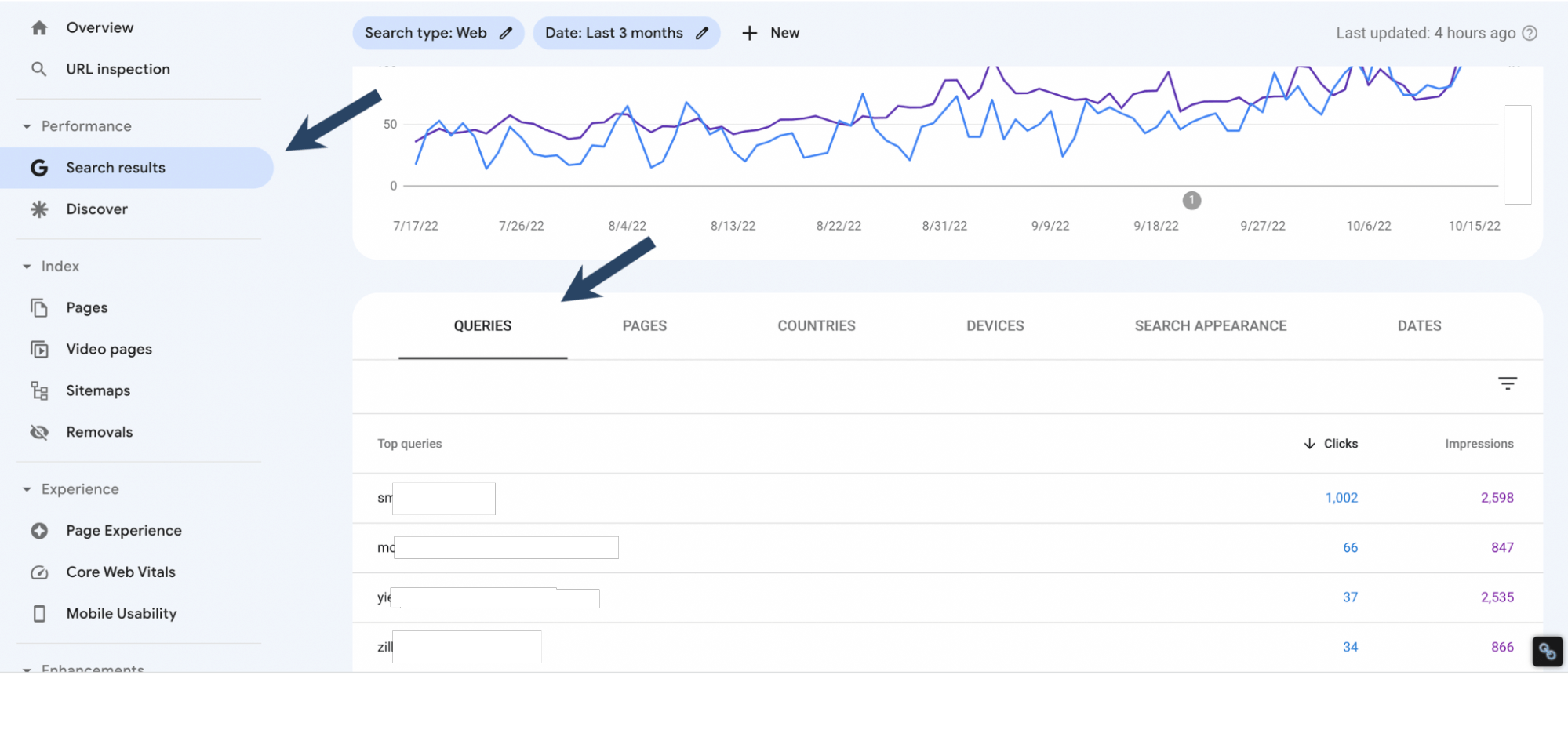
Within the list of keywords shown below the graph, click on the one you intend to diagnose for cannibalization.
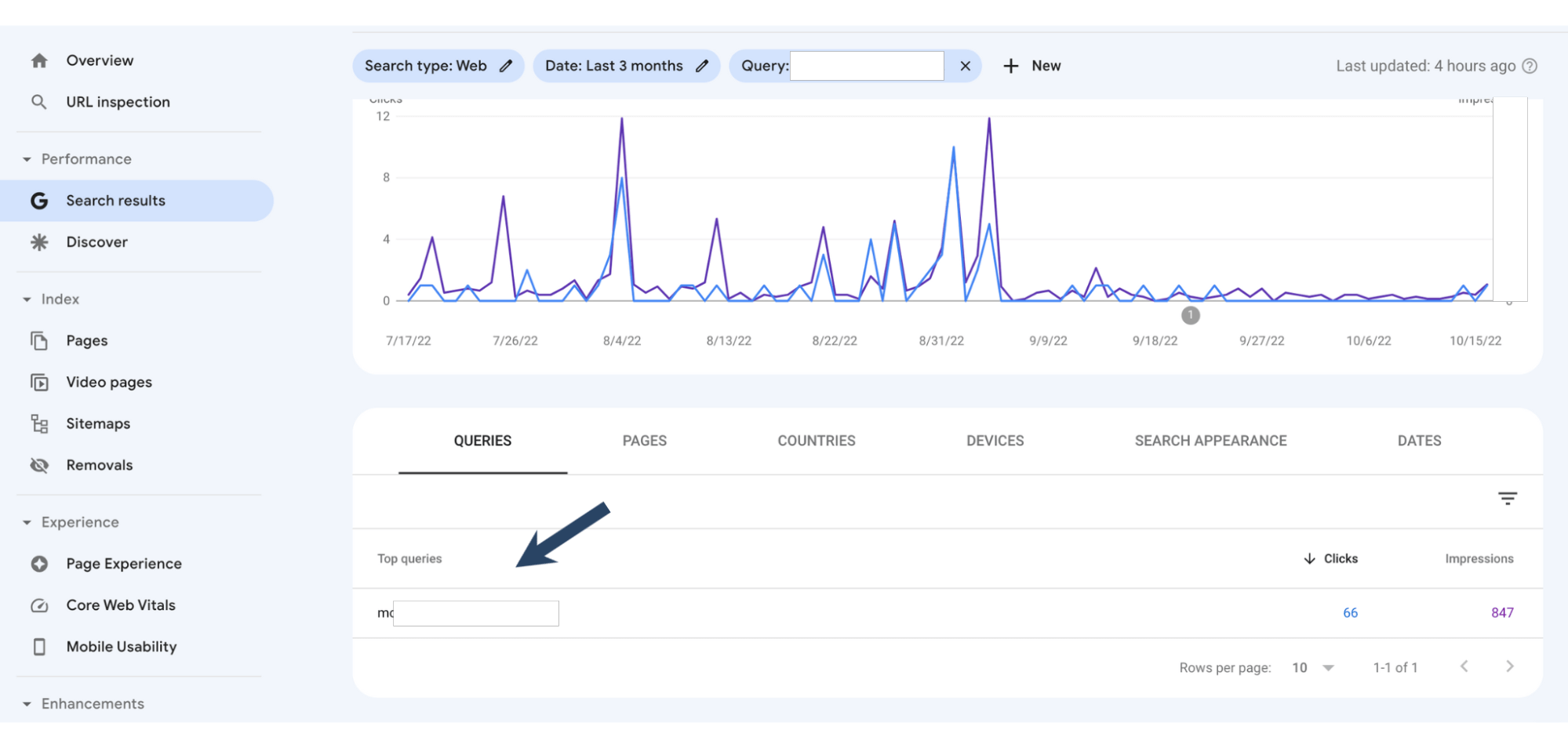
From here, click on the "Pages" option. This way, you will be shown which URLs the keyword ranks for.
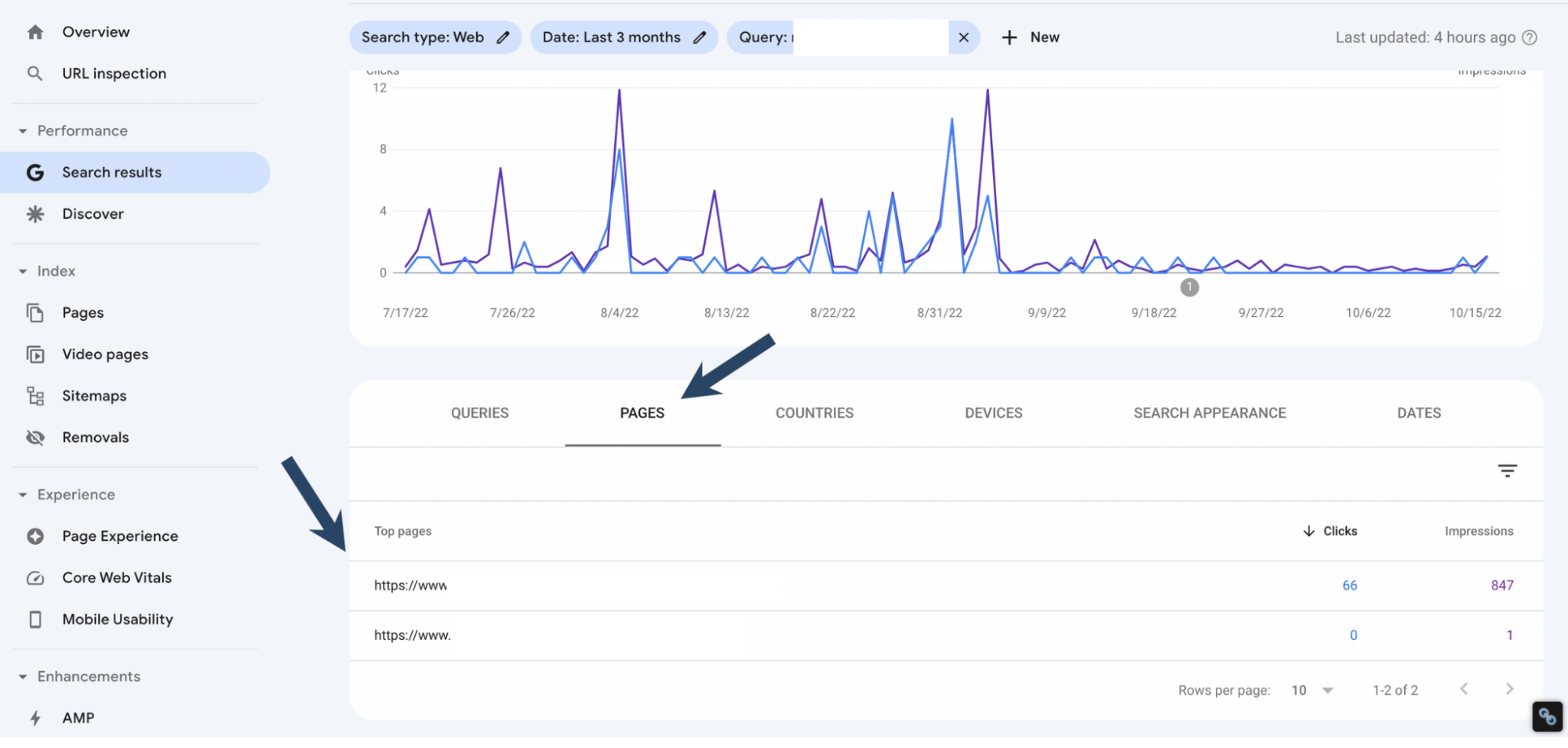
If it is positioning for two or more different pages of your website, you likely have keyword cannibalization.
Ahrefs Trick
Ahrefs is a great SEO tool to help you discover keyword cannibalization for similar pages. The Organic Keywords feature on Ahrefs gives instant access to historical data for specific keywords to spot cannibalization issues.
Click on “Show History Chart” to show your ranking graph.
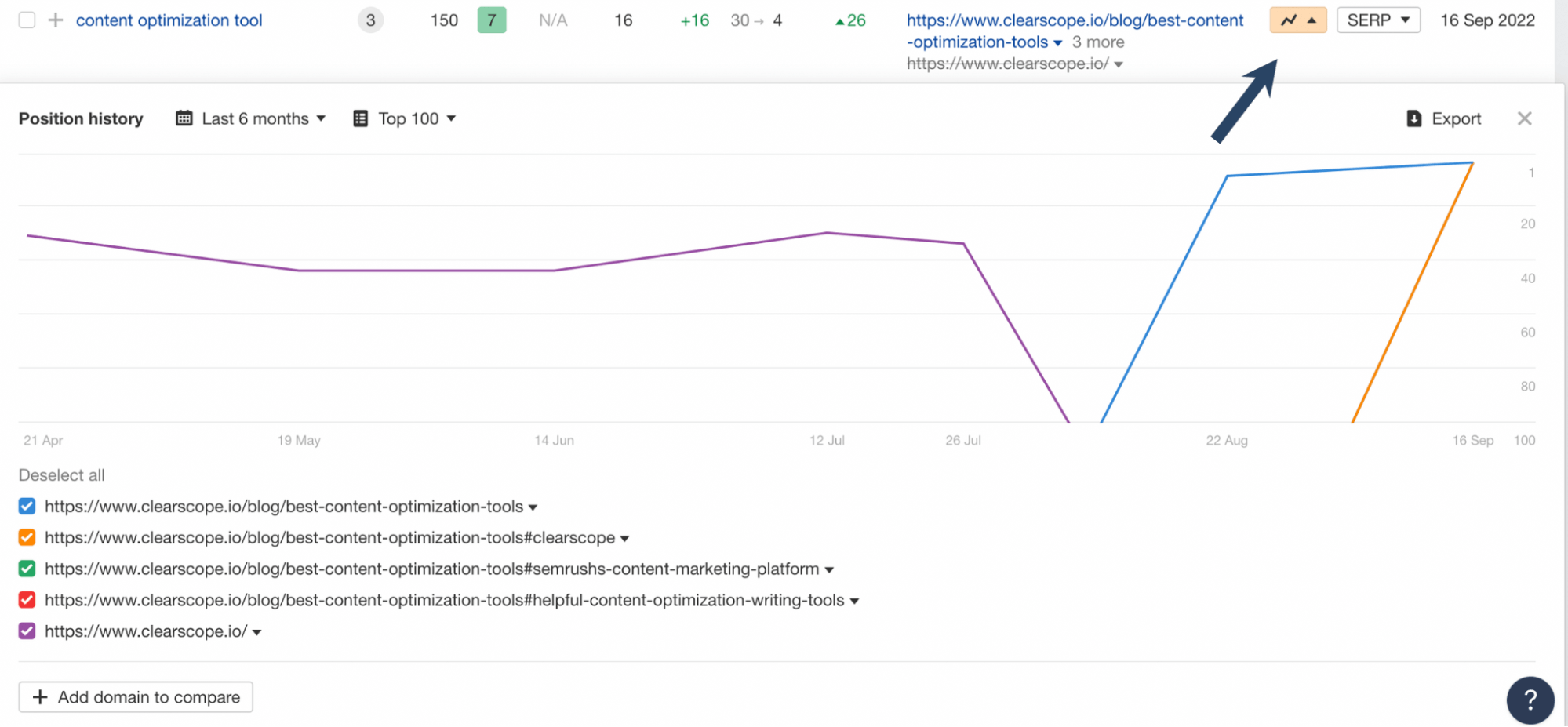
The position history of “https://www.clearscope.io/blog/best-content-optimization-tools” in Ahrefs.
Each color on the graph represents a different URL on your website. Your keywords are cannibalized if you see more than one color.
Mapping Your Customer’s Purchase Journey
Mapping out your buyer’s journey is important for judging the business value of keywords and developing a marketing strategy. The buyer’s journey is the process people go through before purchasing. A sales funnel describes your customer’s journey—from being unaware of the product to buy it.
Stages of the sales funnel
Here’s a popular buyer’s journey framework:
Top of the funnel (awareness stage) – People look for knowledge on the topic in general i.e. “what is coffee”
Middle of the funnel (interest & consideration stage) – People are looking up options for fixing their problem or issue i.e. “best black coffee”
Bottom of the Funnel (conversion stage) – People are trying to buy a particular product or service i.e. “buy black coffee”
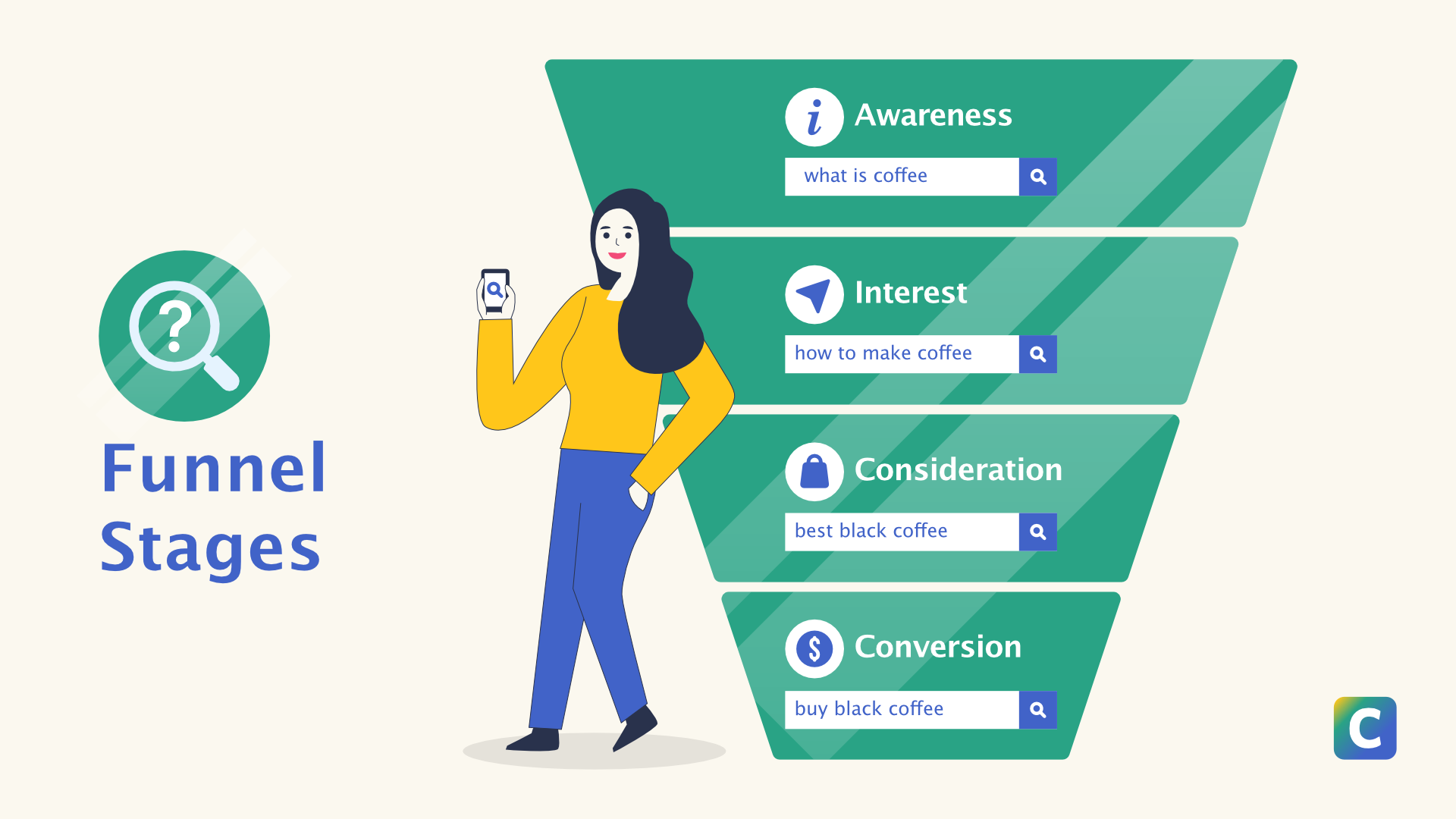
The stages of a marketing funnel.
A person looking for more top-of-funnel keywords is far from purchasing a product or service.
These keywords have a lot more search volume than bottom-of-the-funnel and long-tail keywords.
Someone looking up search terms related to buying has a lot more business value as they produce more sales.
When doing your keyword map, you’ll want to identify the correct search intent for every funnel stage.
Mapping keywords for the awareness stage
In this stage of the buyer’s journey, they acknowledge they may have a problem or challenge. So, they search to learn more about a subject or topic and the different problem areas.
Informational content serves the buyer in the awareness stage.
You should not try to sell your product or service to the user. Instead, you should provide as much value to the user through your content. You'll build trust with your visitors if your business can appear for many informational queries and provide value.
You can find informational intent keywords with these modifiers.
how
what
who
what
why
guide
tutorial
tips
examples
resource
benefits
Instructions
Mapping keywords for the interest stage
In the interest stage, your customers are more aware of their problems. Their clarity on the issue allows them to focus their search for a specific problem while looking for answers.
The customer would have found the solution in the shape of a good or service along with the solution providers.
Since they know where to go to solve their problems, their search requests are navigational.
Specific brand names
Brand product pages
Service names
Locations
Go
Mapping keywords for the consideration stage
In the consideration stage, the user knows their problem and wants to finalize their solution. They would want to compare different options or read reviews about them. Content that helps the user investigate solutions to their problem is best at this stage.
Think of more product or service reviews and comparison keywords with the modifiers:
vs
versus
best
top
review
reviews
Mapping keywords for the conversion stage
They're ready to purchase at the bottom of the funnel or conversion stage. They are keywords users search for towards the end of their buying or purchase journey. So, the keywords would be transactional.
When creating content to satisfy conversion keywords, include resources to push the user to get through the transaction quicker i.e. discount codes or free trials.
Here are modifiers for conversion intent keywords:
Buy
Offer
Near me
Coupon for/ discount
Cheap
For Sale
Price
Pricing
When you match a keyword to your homepage, try making it as detailed or “bottom-of-funnel” as possible. If someone searches a long tail keyword for a product or service and your page appears for precisely what they are looking for, there will be much higher conversions.
It’s time to map keywords!
There you have it. We reviewed how to keyword map, identify keyword cannibalization, and tricks to map keywords to the buyer’s journey.
A proper keyword map would help you keep a clean site structure, plan an effective content strategy to attract the right organic traffic, and save you a lot of time in the future.
Try Clearscope today to help you with the keyword mapping process. Our tool will help you group keywords together with the right search intent.
On-Page SEO: What it is, Why it Matters, & How To Optimize
Here’s what industry experts have to say about on-page SEO. Learn what it is, why it’s important, and how to use it to improve your organic traffic.
Read moreB2B Content Marketing Strategy: Steps to a Winning Strategy
Learn how to create a B2B content marketing strategy that doesn’t just increase brand awareness, but also drives leads, revenue, and customer loyalty.
Read moreTopic Clusters: What Are They? Do They Help Your SEO? (with Video)
Learn how to implement a topic cluster strategy with our step-by-step guide plus a video.
Read more